-40%
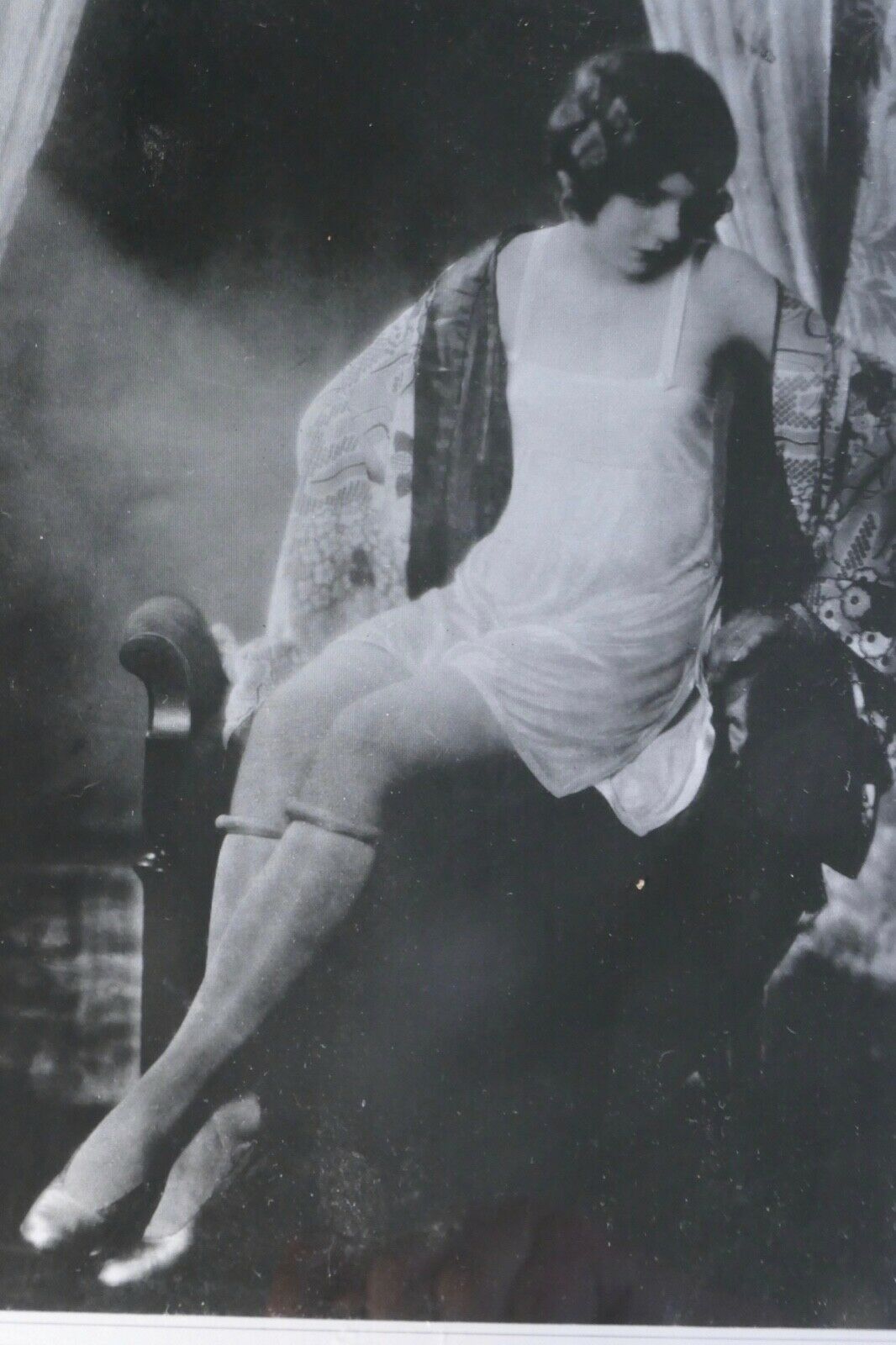
ANTIQUE ADVERTISING MUNSINGWEAR LINGERIE GLASS NEGATIVE PLATE 1900'S
$ 211.2
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
MUNSINGWEAR COMPANYHistory
The company was started by George D. Munsing, who came to Minnesota from New York in 1886 to set up a textile factory, along with Frank H. Page and Edward O. Tuttle from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.[1] Munsing had been superintendent of the Rochester Knitting Works and had experimented with knit fabrics and ribbing, developing a process to plate silk on wool,[1] thus making woolen long underwear, essential in cold climates, "itchless": much more comfortable. Munsing came to Minnesota to set up his factory, which manufactured products for both men and women, because it was in the coldest region of the U.S., and the market for warm underwear would presumably be best there.[2] Munsing also thought that the many Scandinavian immigrants in Minnesota would make it a suitable location; mention of underwear was taboo in American society at the time.[3] Patent attorney Amasa C. Paul served as Northwestern Knitting Company's president when it was incorporated in February 15, 1887, and Munsing was vice-president.[1] The Northwestern Knitting Company's ad for its products in the September 1897 issue of Ladies' Home Journal was the first to display underwear on a live model.[4]
Munsing was a technologist and the company received several patents, including those for a crocheting machine in 1891 and a union suit in the early 1890s. The union suit was the company's flagship product until the 1920s,[5] when central heating made it less useful.[6] It continued until 1969.[7] The cream-colored garment became iconic and was featured in the company's advertising with children and adults outfitted in them; underwear ads had never used live models before.[8] In 1894 Munsing left the company.[1]
In 1923 the company went public and changed its name to Munsingwear, Inc.[1] At the time it was the largest manufacturer of underwear in the world.[9] Its slogan was "Don't say underwear, say Munsingwear".[10] At its peak it was producing 30,000 garments per day.[11] Its knitting mill was the largest west of the Alleghany Mountains.[12] The company expanded into women's underwear in the 1920s, and starting in 1931 offered Foundettes, which used an elasticized yarn to produce a combination foundation garment that combined a brassiere and a girdle.[13]
Munsingwear was the largest employer of women in the state of Minnesota; at one point 85% of its 3,000 employees were women.[14] By the 1920s, in part trying to avoid unionization, Munsingwear offered many benefits, some quite progressive for the time. It had a health clinic staffed by a full-time nurse, with regular visits from general practitioners, otolaryngologists (because of air quality problems), dental assistants, and dentists. All of this care was free.[15] Mungsingwear also offered access to health insurance, a branch of the Minneapolis Public Library which circulated 7,500 books a year, a large, fully staffed kitchen which provided lunches to the entire work force (in shifts),[16] an orchestra which performed during Thursday lunch breaks, an on-site gymnasium, sports teams,[17] and other benefits.[2][18][19]
Its flagship product of recent years, patented in 1943,[20] was the "Kangaroo brief", featuring a horizontal fly and a contoured pouch. For an advertisement showing all its styles of men's underwear available in 1969, see
In 1951 the company merged with the Vassar Swiss Underwear Company, which became the Vassar division of Munsingwear.
In 1955 the company began producing its Grand Slam gold shirt, with a Penguin logo. In the 1960s and 1970s these were the best-selling golf shirts in the world. Munsingwear also added a line of women's golf, bowling, and fashion shirts.
In 1991 the company filed for Chapter 11 reorganization. In 1996 it changed its name to PremiumWear, and focused on specialty markets. Premiumwear was in turn bought by the Canadian clothesmaker John Forsythe, which sought bankruptcy protection in 2013. The Munsingwear and Original Penguin brands are currently owned by Perry Ellis.
Vassar Swiss Underwear Company
Vassar Swiss Underwear Company began operations in 1900 and was purchased by Northwestern Knitting Company in 1912.
The founders were George E. Rutledge, Emil A. Basener, and Frederick S. McCoy. The company started in Chicago, but soon moved operations to Rochelle, Illinois. Shortly after the sale, Northwestern decided to ramp up production and moved Vassar Swiss back to Chicago, building a new plant, named the Vassar Swiss Underwear Company Building.[25] Construction was completed in April of the following year. Vassar Swiss prospered in its new location. Rutledge, now a vice-president at parent company Northwestern, joined with other company designers to improve his original union suit design.[25] In 1923, the company constructed an addition on the western portion of their building, by the same architect, to house their box factory and shipping.
Over the next four decades, the company shifted focus and products. Union suits became less popular, and briefs soon became the company's leading product. Vassar Swiss purchased the building from Stewart, after having leased it since construction
Rutledge retired in 1937. The company shortened its name to "Vassar Company" and, in 1951, "Vassarette."[26] In 1967, production operations were moved from Chicago to Paris, Texas,[25] and as of 2010 the Vasarette name is owned by Vanity Fair Brands, and produces women's underwear.